Exotic Spartina alterniflora invasion increases CH4 while reduces CO2 emissions from mangrove wetland soils in southeastern China
Abstract
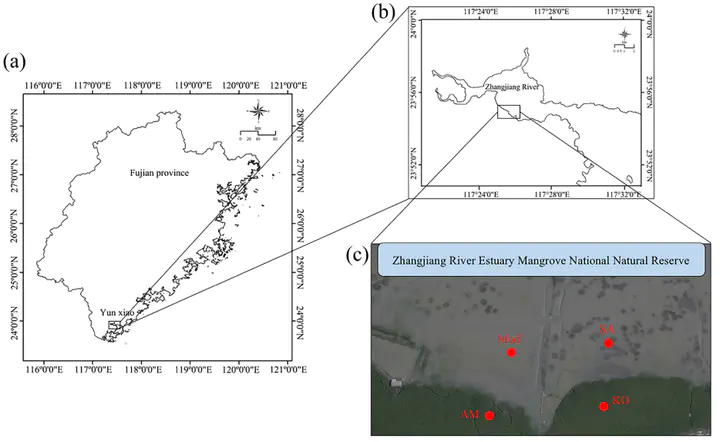
Mangroves are critical in global carbon budget while vulnerable to exotic plant invasion. Spartina alterniflora, one of typical salt marsh plant grows forcefully along the coast of China, has invaded the native mangrove habitats in Zhangjiang Estuary. However, the effects of S. alterniflora invasion on soil carbon gases (CH4 and CO2) emission from mangroves are not fully understood. Accordingly, we conducted a field experiment to investigate the soil CH4 and CO2 emission during growing seasons in 2016 and 2017 at four adjacent wetlands, namely bare mudflat (Mud), Kandelia obovata (KO), Avicennia marina (AM) and S. alterniflora (SA). Potential methane production (PMP), potential methane oxidation (PMO), functional microbial abundance and soil biogeochemical properties were measured simultaneously. Our results indicate that S. alterniflora invasion could dramatically increase soil CH4 emissions mainly due to the enhancement in PMP which facilitated by soil EC, MBC, TOC and mcrA gene abundance. Additionally, S. alterniflora invasion decreases soil CO2 emission. Both heterotrophic microbial respiration (16S rRNA) and methane oxidation (pmoA and ANME-pmoA) are responsible for CO2 emission reduction. Furthermore, S. alterniflora invasion greatly increases GWP by stimulating CH4 emissions. Thus, comparing with mangroves, invasive S. alterniflora significantly (p < 0.001) increases CH4 emission while reduces CO2 emission.